- 路 Microwave
- 路 Atmospheric Pressure Microwave 路 Pressure Microwave 路 Parallel Microwave
- 路 Ultrasonic 路Low Temperature Ultrasound
- 路 Ultraviolet Light
- 路 Microwave Heating 路 Atmospheric Pressure Synthesis 路 Atmospheric Pressure Catalysis 路 Atmospheric Pressure Extraction
- 路 Sample Preparation 路 Microwave Digestion
- 路 Soil Digestion 路 High Pressure Synthesis
- 路 Solid Phase Synthesis
- 路 Organic Synthesis
- 路 Ionic Liquid Synthesis
- 路 Degradation Of Natural Organic Matter
- 路 Natural Product Extraction / Purification
河北祥鹄科学仪器有限公司
115 A novel one-pot strategy to prepare β-cyclodextrin functionalized capillary monoliths for enantioseparation of basic drugs
This paper, written by researchers from Shenyang Pharmaceutical University and others, discusses A novel one-pot strategy to prepare β-cyclodextrin functionalized capillary monoliths for enantioseparation of basic drugs. The paper is published in an important journal < Talanta >. IF:4.244.
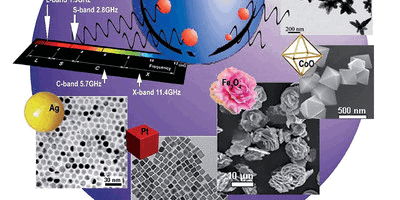
In recent years, the research work of microwave chemical instrument used in the synthesis of materials has become a hot direction of scientific research, which has been paid great attention to by many scholars!
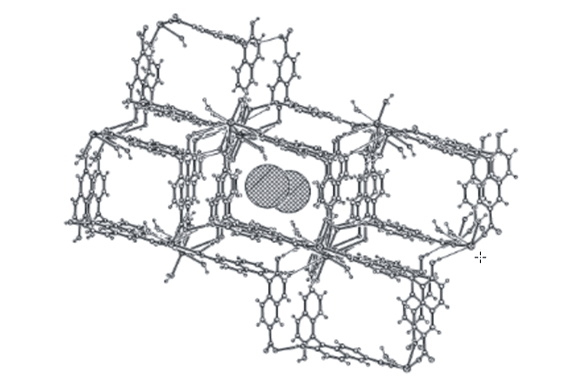
With native -cyclodextrin (β-CD) added into the polymerization mixture directly, a novel, convenient and lowcost one-pot strategy was developed to prepare the β-CD functionalized organic polymer monolithic capillary column. Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU) as a basic catalyst for the ring opening reaction between β-CD and glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) was introduced into the polymerization system for the first time. Thereby, two consecutive reactions namely the in situ methacrylation of β-CD and copolymerization reaction can be achieved in one pot. The preparation conditions including the type and composition of porogens,the ratio of functional monomer to crosslinker and amount of 2-acrylamido-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid (AMPS) were optimized. The specific surface area and morphology of the prepared monolith were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and nitrogen adsorption analysis, respectively. Raman spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy confirmed that β-CD was covalently bonded onto the monolith successfully. Then, the monolithic column was applied to enantioseparation of six basic drugs in capillary electrochromatography (CEC). Under the optimal conditions, tropicamide, homatropine, homatropine methylbromide, brompheniramine, chlorpheniramine and clorprenaline were all totally separated with the resolution (Rs) values of 2.84, 4.70, 4.61, 3.01, 2.57 and 2.33, respectively. Furthermore, the column demonstrated satisfactory stability and repeatability of retention time and enantioselectivity using homatropine as model analyte.

Fig.1/4↑

Fig.2/4↑
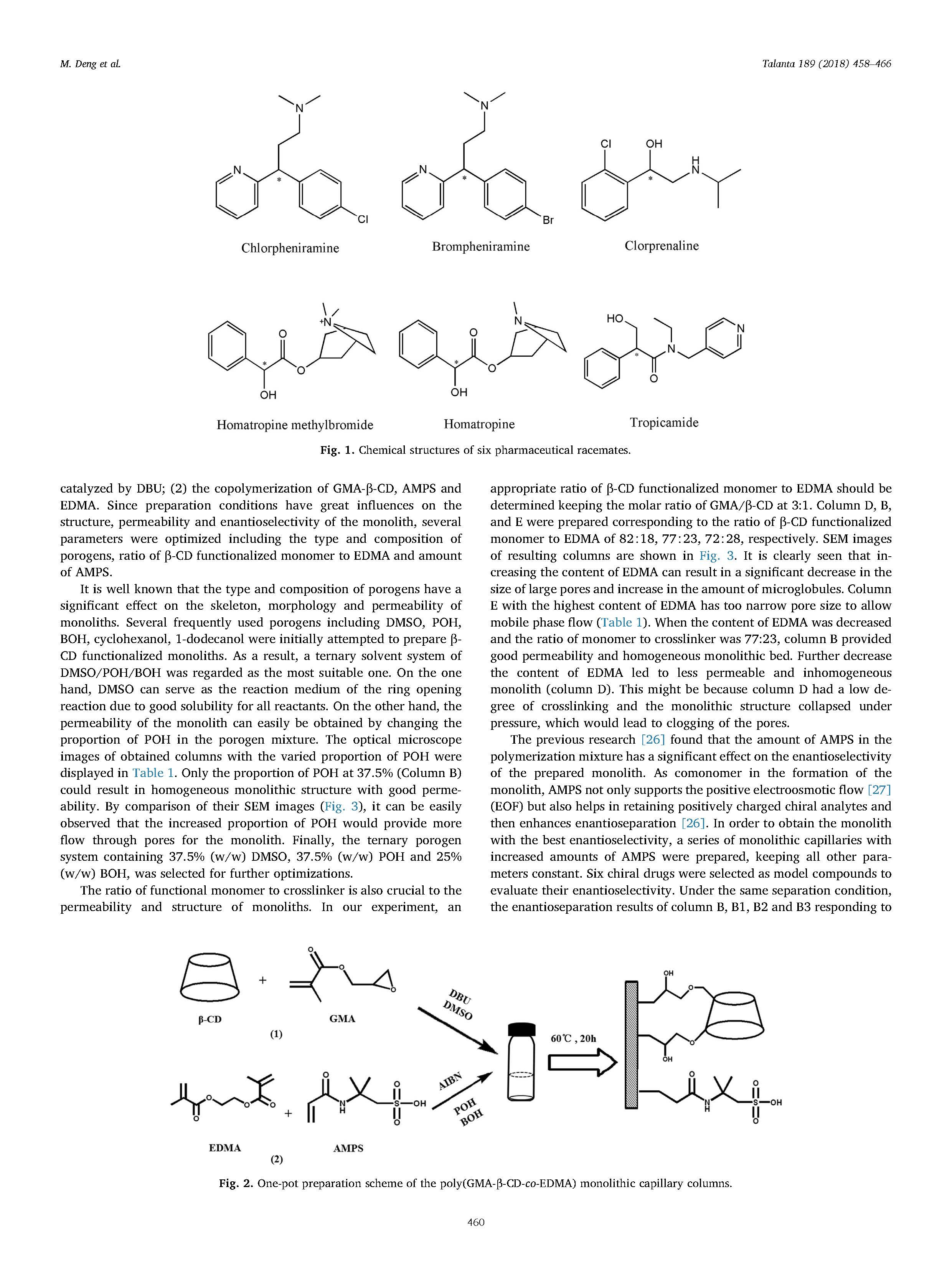
Fig.3/4↑
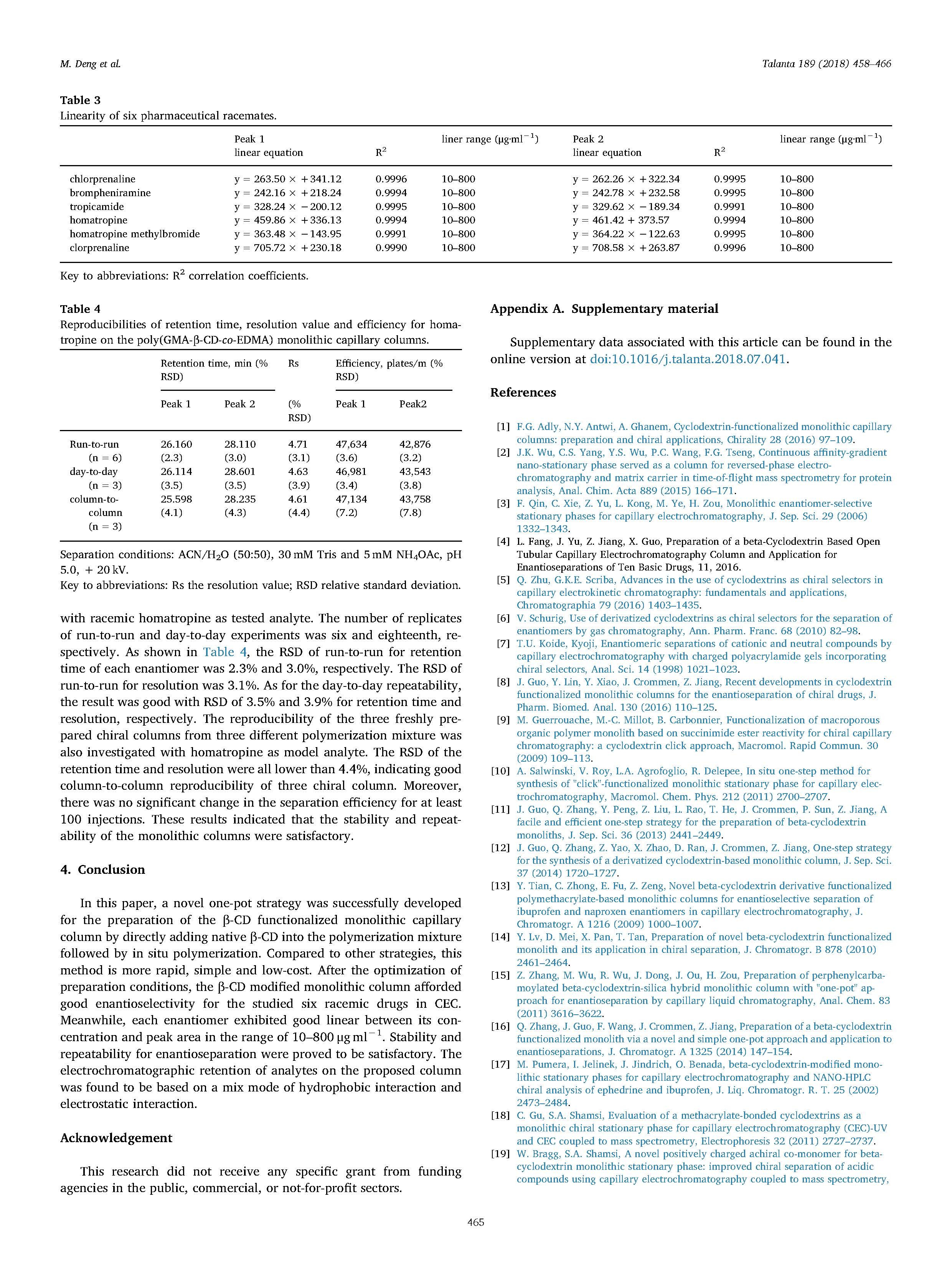
Fig.4/4↑
In this paper, a novel one-pot strategy was successfully developed for the preparation of the β-CD functionalized monolithic capillary column by directly adding native β-CD into the polymerization mixture followed by in situ polymerization. Compared to other strategies, this method is more rapid, simple and low-cost. After the optimization of preparation conditions, the β-CD modified monolithic column afforded good enantioselectivity for the studied six racemic drugs in CEC. Meanwhile, each enantiomer exhibited good linear between its concentration and peak area in the range of 10–800 μgml−1. Stability and repeatability for enantioseparation were proved to be satisfactory. The electrochromatographic retention of analytes on the proposed column was found to be based on a mix mode of hydrophobic interaction and electrostatic interaction.
All CEC experiments were performed on a CE apparatus (CL1030, Beijing huayanglimin instrument Co., Ltd, Beijing, China). A syringe pump (SPLab04, Shenchen Precision Pump Co., Ltd, Baoding, China) was used to pump liquid through fused-silica capillaries. An HPLC pump (PU-1580, Jasco corporation, Japan) was used to flush monolithic columns with mobile phase for conditioning. The fused-silica capillaries (375 μm o.d.×75 μm i.d.) were purchased from Ruifeng Chromatography Ltd. (Yongnian, Hebei, China). A microwave-ultrasound combined reactor (XH-300A, Beijing Xianghu Technology Co., Ltd.) provided continuous and homogeneous ultrasound and microwave irradiations. Morphological characterizations of monoliths were taken with a Hitachi S4800 scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Ltd., Japan) after a gold coating of the samples. Microscopic pictures were taken with an Olympus microscope (BX60, Olympus, Germany). Raman spectra of monolithic materials (confined within capillary support) were obtained with a HORIBA labRAM HR Evolution raman spectrometer (Horiba Group, Japan) equipped with an Olympus objective LMPLAN FLN 50/0.5 and a double-frequency Nd: YAG laser (532 nm). The specific surface area was examined by nitrogen adsorption experiment on a Micromeritics TriStar II Plus apparatus (Micromeritics Instrument Ltd, USA). Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy was obtained with a Bruker Ultrashield Plus 600 MHz spectrometer (Bruker Corporation, Switherland).







































 京ICP备15050585号
京ICP备15050585号

