- 路 Microwave
- 路 Atmospheric Pressure Microwave 路 Pressure Microwave 路 Parallel Microwave
- 路 Ultrasonic 路Low Temperature Ultrasound
- 路 Ultraviolet Light
- 路 Microwave Heating 路 Atmospheric Pressure Synthesis 路 Atmospheric Pressure Catalysis 路 Atmospheric Pressure Extraction
- 路 Sample Preparation 路 Microwave Digestion
- 路 Soil Digestion 路 High Pressure Synthesis
- 路 Solid Phase Synthesis
- 路 Organic Synthesis
- 路 Ionic Liquid Synthesis
- 路 Degradation Of Natural Organic Matter
- 路 Natural Product Extraction / Purification
河北祥鹄科学仪器有限公司
252 Optimization of ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction of oligosaccharides from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds
This paper, written by researchers from Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University and others, discusses Optimization of ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction of oligosaccharides from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds. The paper is published in an important journal < Fuel >. IF:4.908.
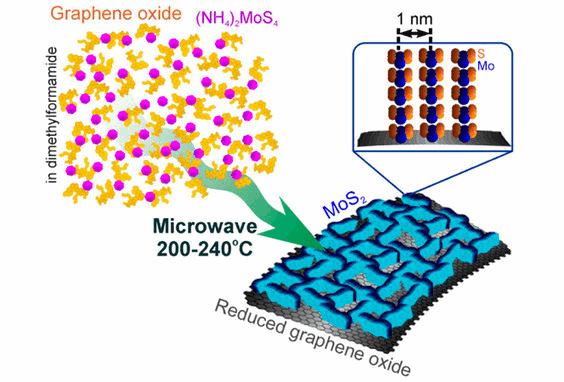
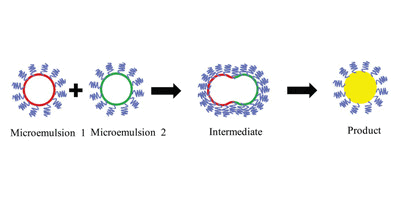
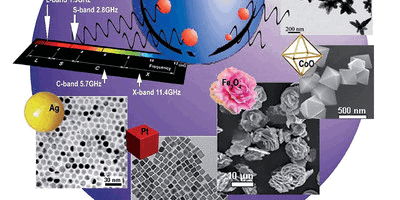
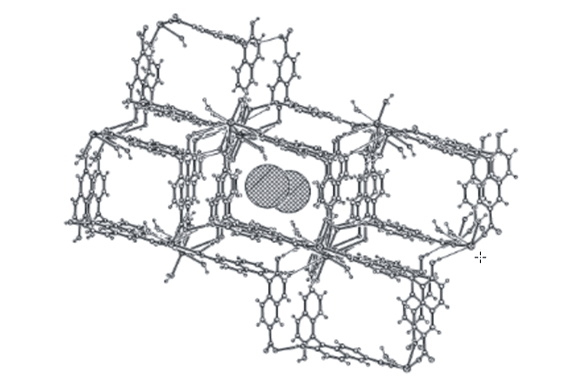
In recent years, the research work of microwave chemical instrument used in the synthesis of materials has become a hot direction of scientific research, which has been paid great attention to by many scholars!
The traditional technology replaced by ultrasonic or microwave assisted extraction has attracted considerable research interest. In order to maximize the yield of different degree polymerized oligosaccharides from lotus seeds, response surface methodology (RSM) was applied for optimization by ultrasound-microwave assisted extraction (UMAE) in this study. The results indicated that the optimal conditions for UMAE of lotus seed oligosaccharides were: extraction time 325.00 s, liquid-solid ratio 10.00 mL/g (L/S ratio), ultrasonic power 300.46 W, microwave power 250.00 W, and the yield of total oligosaccharides, trisaccharides, and tetrasaccharides was increased by 76.59%, 17.47%, and 27.21%, respectively. On the other hand, the extraction time was shortened by 12.18, 8.92, and 1.16 times, respectively, compared to the hot water extraction, ultrasonicassisted extraction (UAE), and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE). These results confirmed that UMAE has a greater potential and efficiency for extraction of oligosaccharides than traditional hot water, ultrasonic or microwave assisted extraction alone.

Fig.1/4↑

Fig.2/4↑

Fig.3/4↑

Fig.4/4↑
UMAE is an effective technology for the extraction of prebiotic oligosaccharides from lotus seeds. RSM was successfully implemented for the optimization of extracting the total oligosaccharides, trisaccharides, and tetrasaccharides from lotus seeds. The results showed that the optimum processing conditions of ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction for lotus seed oligosaccharides were: extraction time 325.00 s, liquid-solid ratio 10.00 mL/g, ultrasonic power 300.46 W, and microwave power 250.00 W. The yield of gross lotus seed oligosaccharides, trisaccharides, and tetrasaccharides under such conditions was theoretically predicted as 3.016%, 3.947%, and 4.894%, respectively. It increased by 76.59%, 17.47%, and 27.21%, respectively, whereas the extraction time shortened by 12.18 times, 8.92, and 1.16 times, respectively, compared to the extraction process through traditional warm water soaking, ultrasonic assisted, and microwave-assisted extraction.
Quick-frozen fresh lotus seeds were thawed for 1 h and dried in an air circulatory tray (DHG-9030, Tayasaf, Beijing, China) after they were cored. The lotus seeds were subjected to drying at 50 °C to retain only about 7% of original water content. The desiccated lotus seeds were crushed with a mill (FW-80, Taisite Co., Tianjin, China), sifted through 60 meshes (pore size 0.3 mm), and stored as experimental raw material. Dried lotus seed powder and deionized water were mixed for liquidsolid ratio =5 (v/w). Guo et al. (2015) described a method to separate the starch in the lotus seeds to exclude the influence of ultrasonic degradation for the oligosaccharides yield (Machado et al., 2015). Then the starch-depleted test sample solution was added to 150 mL constant volume at the liquid-solid ratio (L/S ratio) applied in the response surface design before it was transferred to a heterotype three-port glass vase in the device and subjected to ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction (XH-300B, Beijing Xianghu, Beijing, China). Upon the completion of the reaction, the extracted solution was vacuum aspirated, and the residue discarded. The filtrate was speed vacuum concentrated (BUCHI 409, Buchi Corp., New Castle, DE, USA) and 95% ethanol was added to three volumes of the test liquid, followed by overnight incubation at 4 °C and centrifugation (L530, Xiang Yi Centrifuge Instrument Co., Ltd. Changsha, China) The supernatant was freeze-dried to powder consistency for subsequent processes.







































 京ICP备15050585号
京ICP备15050585号

