- 路 Microwave
- 路 Atmospheric Pressure Microwave 路 Pressure Microwave 路 Parallel Microwave
- 路 Ultrasonic 路Low Temperature Ultrasound
- 路 Ultraviolet Light
- 路 Microwave Heating 路 Atmospheric Pressure Synthesis 路 Atmospheric Pressure Catalysis 路 Atmospheric Pressure Extraction
- 路 Sample Preparation 路 Microwave Digestion
- 路 Soil Digestion 路 High Pressure Synthesis
- 路 Solid Phase Synthesis
- 路 Organic Synthesis
- 路 Ionic Liquid Synthesis
- 路 Degradation Of Natural Organic Matter
- 路 Natural Product Extraction / Purification
河北祥鹄科学仪器有限公司
249 Simultaneous microwave/ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction ofantioxidant ingredients from Nitraria tangutorun Bobr. juiceby-products
This paper, written by researchers from Northeast Normal University and others, discusses Simultaneous microwave/ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction ofantioxidant ingredients from Nitraria tangutorun Bobr. juiceby-products. The paper is published in an important journal < Industrial Crops and Products >. IF:3.849
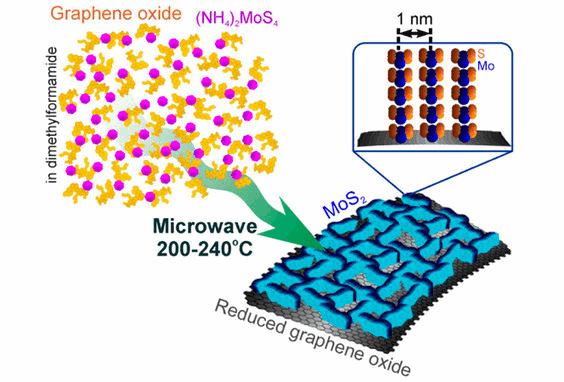
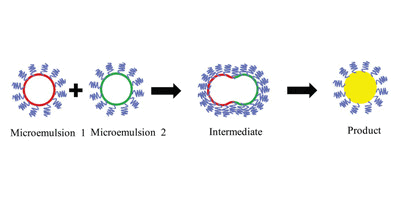
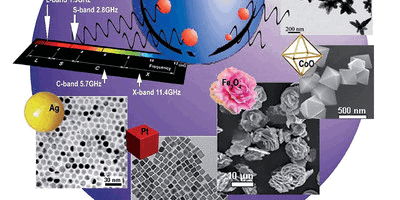
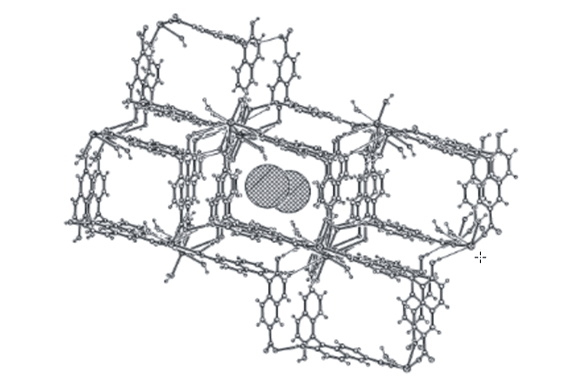
In recent years, the research work of microwave chemical instrument used in the synthesis of materials has become a hot direction of scientific research, which has been paid great attention to by many scholars!
By-products originating from food processing are a considerable disposal problem for the foodindustry. Because of the absence of specifically effective processing technology, huge quantities of by-products are often abandoned as rubbish and prone to microbial spoilage. Given this, a simultaneousmicrowave/ultrasonic assisted enzymatic extraction (SMU-AEE) method was established for the firsttime, and performed for antioxidant ingredients extraction from Nitraria tangutorum juice by-products(NJB) in the present study. Its experimental conditions were optimized by single factor test and responsesurface methodology (RSM), and gave the corresponding response values for antioxidant capacity of NJBextract (NJBE) of 219.73 ± 7.03 mg TE/g, which was 27.62%–190.23% higher than those obtained by tra-ditional extraction methods. Chemical composition assay suggested that the increasing of antioxidantcapacity of NJBE by SMU-AEE was because of the improvement of extraction efficiency of antioxidantingredients from NJB, including phenols, flavonoids and anthocyanins. Furthermore, oxidative injuryprotection ability assay showed that NJBE was good at protecting cells from UVB-oxidative phototoxic-ity and doxorubicin-oxidative cardiotoxicity, and its protecting ability surpasses or approaches to that ofgrape seed extract (GSE, the positive control drug), indicating its good potential to be a natural antioxidantin food and pharmaceutical industries.

Fig.1/4↑

Fig.2/4↑

Fig.3/4↑

Fig.4/4↑
In the present study, SMU-AEE method, a combined applicationof three assisted techniques including microwave, ultrasonic andenzyme extraction, was established for antioxidant ingredientsextraction from berry juice by-products for the first time. After opti-mizing by single factor test and RSM, the experimental conditionsfor antioxidant ingredients extraction from NJB were established tobe 70% ethanol extraction solvent, 0.6% added content of cellulase,pH 4.5 of phosphate buffer, ultrasonic power 800 W, microwavepower 420 W, ratio of solvent to NJB 20:1, extraction temperature66◦C and extraction time 43 min, and gave the correspondingvalue for antioxidant capacity of NJBE of 219.73 ± 7.03 mg TE/g,which was 27.62%–190.23% higher than traditional extractionmethods. Chemical composition assay showed that the contents ofphenols, flavonoids, and anthocyanins of NJBE by SMU-AEE were,respectively, 25.06%–141.48%, 8.86%–133.52, and 9.81%–92.42%higher than those by traditional extraction methods, suggestingthat the increasing of antioxidant capacity of NJBE by SMU-AEEwas the result of the improvement of the extraction efficiency ofantioxidant ingredients from NJB. Moreover, NJBE exhibited excel-lent cell protection effect from UVB-oxidative phototoxicity anddoxorubicin-oxidative cardiotoxicity, indicating its good potentialto be a natural antioxidant in food and pharmaceutical industries.
For the extractions, 1 g of dried NJB powder was mixed with10 mL of solvent in a glass flask, which were duly covered toavoid solvent loss, and placed in a microwave/ultrasonic syner-gistic extraction apparatus (XH-300B, Beijing Xianghu Science andTechnology Development Co., Ltd. China). The reaction mixture wassimultaneously irradiated at 300 W of microwave power and 600 Wof ultrasonic power at a temperature of 60◦C for a fixed reactiontime of 20 min. Upon completion of the treatment, the resultingmixture was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 15 min. The supernatantwas collected and vacuum dried at 30◦C, generating N. tangutorumjuice by-products extract (NJBE). NJBE was dissolved in 10 mL ofwater, and then purified on an AB-8 macroporous resin column bysuccessively elution with water and ethanol. The ethanolic eluatewas collected and vacuum dried at 30◦C, and redissolved in waterfor antioxidant assay.







































 京ICP备15050585号
京ICP备15050585号

